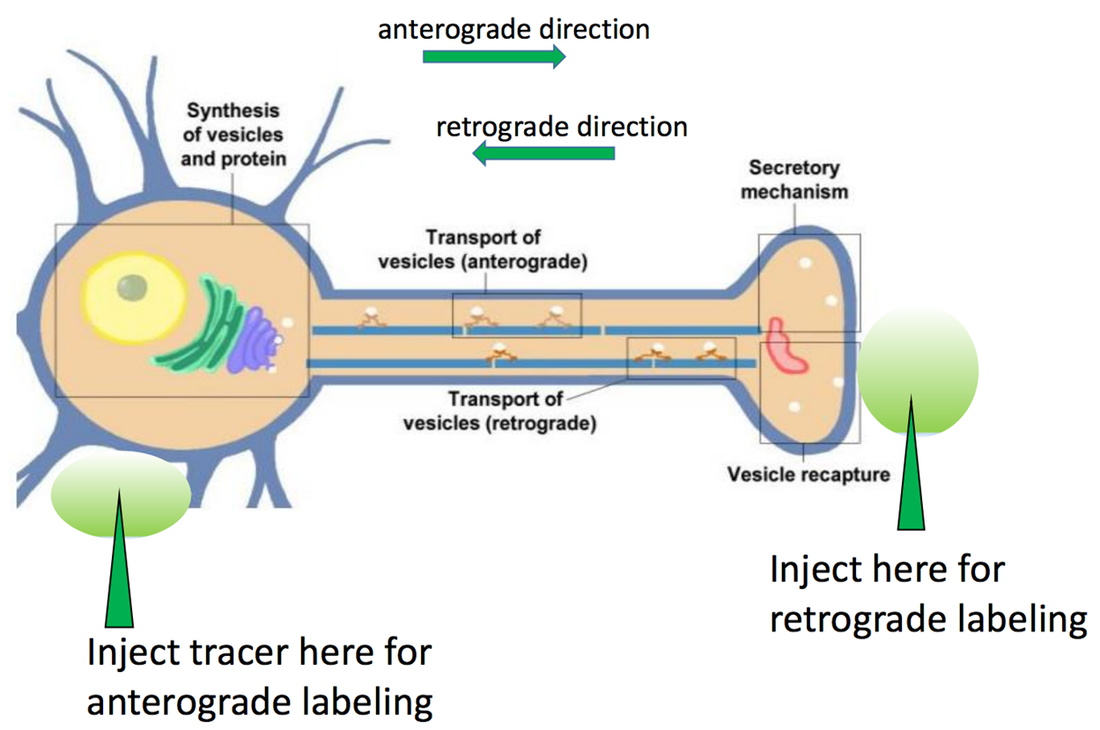
A central task in neuroscience is to identify the "cables" connecting each brain region, understand the connections supporting the communication of information between them, and assess the presence of synaptic connections whose activity we can manipulate in order to address their causal role in neural activity, and animal behavior.
For this we use retrograde and anterograde neural tracing methods, using molecular tracing agents such as Cholera Toxin Subunit B conjugated with fluorophores such as Alexa 647, or fluorescent markers delivered by anterograde and retrograde labeling viruses such as AAV9 and rAAV2, by intracerebral injection.
For this we use retrograde and anterograde neural tracing methods, using molecular tracing agents such as Cholera Toxin Subunit B conjugated with fluorophores such as Alexa 647, or fluorescent markers delivered by anterograde and retrograde labeling viruses such as AAV9 and rAAV2, by intracerebral injection.
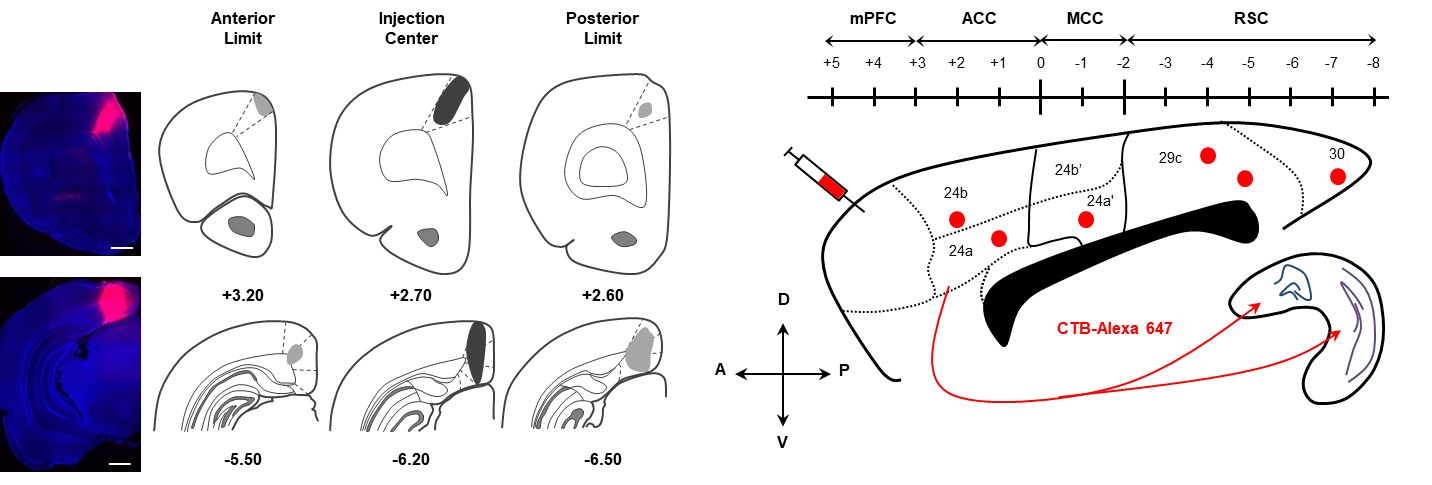
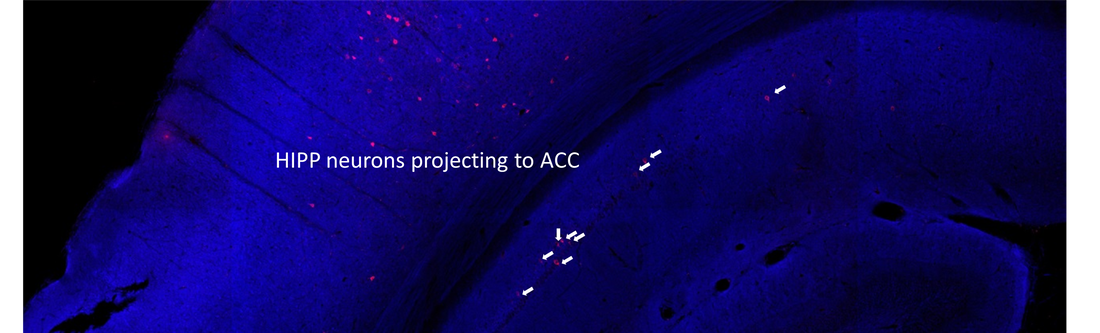
The results of such approach are depicted below, in one example of injection of CTB-Alexa647 in ACC which labels hippocampal neurons in CA1 stratum pyramidale
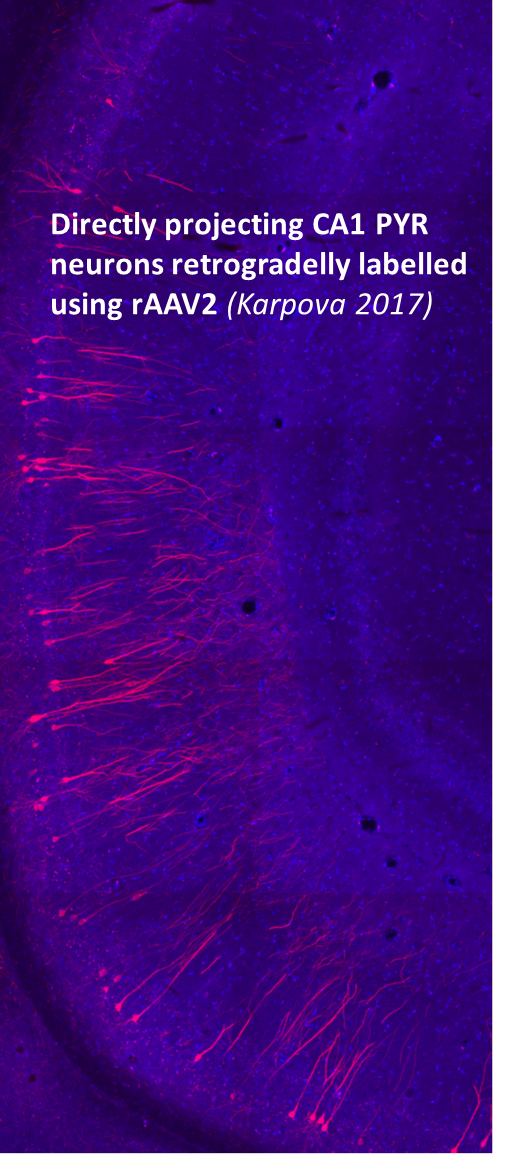
The same result can be achieved by the injection of rAAV2, a retrograde labeling virus carrying tdTomato